Health And Fitness
Tracking Childhood Development: Essential Milestones by Age
Developmental childhood knowledge is the foundation on which the overall growth of a child is shaped. Parents and caregivers are expected to be at the forefront in observing the stages of normal development. However, every child is unique; these milestones serve as guidelines for most children’s development. Early intervention programs show positive impacts when a delay in development is detected. Various strategies can be applied to build language skills and cognitive abilities in a child. Regular monitoring helps document a child’s abilities accurately at each stage. Emphasizing Health and Fitness over appearance ensures the inculcation of positive self-image and healthy habits, leading to a stable Growth Rate in Children.
Infancy (0-12 months)

Image Source: pexels
Physical Development
Motor Skills
Infants exhibit rapid physical growth during the first year. Babies start by gaining control over their head and neck muscles. At three months, most can raise their heads while on their tummies. By six months, most infants can roll over both ways. At nine months, babies often can sit without support and might even start crawling. By twelve months, most infants take their first steps, another significant milestone in motor development.
Sensory Development
Sensory development is an important part of an infant’s early experience. Newborns have a remarkable sense of smell and can distinguish their mother’s odor. In terms of vision, significant development takes place over the following months. By three months, babies can track moving objects with their eyes. Hearing is also well developed. Infants can recognize different sounds and respond to familiar voices. Touch remains the most important way babies feel comfort and bond with their parents; they are pleased with various textures and sensations.
Cognitive Development
Object Permanence
When considering cognitive development in infants, we often look at what is referred to as object permanence: the understanding that objects continue to exist even if they are out of sight. At about six to eight months, babies start to look for hidden objects, showing this cognitive development. This is a major step in memory and understanding the world.
Early Problem-Solving
Infants begin to show early problem-solving skills within the first year. Babies explore through trial and error. For example, dropping a toy several times on purpose to see where it lands or the sound it makes. These actions show cognitive growth and the growing curiosity of the infant. By twelve months, infants can solve simple problems, such as figuring out how to reach a toy just out of reach.
Social and Emotional Development
Attachment
Attachment is the foundation of an infant’s social and emotional development. Secure attachment is developed through consistent and responsive caregiving. Infants show preferences for primary caregivers by smiling, cooing, and making eye contact.
Separation Anxiety
Many infants show the first signs of separation anxiety by six months of age; they start to fuss when their primary caregiver is not in sight. This indicates that the attachment bond is strong by this time.
Early Communication
Early communication skills develop as infants interact with their caregivers. Crying, cooing, and babbling are ways for a baby to express needs and emotions. By six months, many infants recognize their names and respond to simple verbal commands. Around nine months, they start using gestures, such as pointing or waving, to communicate. By twelve months, some infants may say their first words, marking a significant milestone in language development.
Key Findings: According to the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, babies start experimenting with and recognizing sounds, expressing emotions through sounds, and recognizing familiar faces as part of their developmental milestones.
Toddlerhood (1-3 years)
Physical Development
Walking and Running
Toddlers undergo incredible physical changes. Most children walk unaided by 12 to 18 months. By age two, many can run with increased coordination. Repeated practice helps improve balance and movement. Parents should provide opportunities for safe exploration.
Fine Motor Skills
Fine motor skills develop rapidly during toddlerhood. Children start by grasping small objects with their thumb and forefinger. By 18 months, many toddlers can stack blocks and turn pages in a book. By age two, children often start drawing with crayons. These activities develop hand-eye coordination. Playing with small objects supports fine motor development.
Cognitive Development
Language Acquisition
Language acquisition accelerates significantly during the toddler years. Many children utter their first words around 12 months of age. Vocabulary expands rapidly between one and three years. By age two, toddlers are usually forming short sentences. Interaction with children encourages the development of language abilities. Reading to the child stimulates vocabulary growth and comprehension.
Symbolic Play
Symbolic play emerges as a major milestone in cognitive development. In play, toddlers use one object to represent another. For example, a block may be used to represent a car. This type of play illustrates a growing imagination and problem-solving capacity. Encouraging symbolic play fosters cognitive and social development. Providing various toys enhances symbolic play.
Social and Emotional Development
Independence
Autonomy becomes a pressing concern for toddlers. Independence begins to emerge around the age of two. Small independent strides, such as self-feeding or selecting clothes, enable them to become self-reliant. Parents should provide opportunities for independence and praise attempts to encourage further development.
Social Interaction
Social interaction skills develop greatly during toddlerhood. Children start perceiving and responding to the emotions of others. Playdates provide opportunities to practice social behavior. Sharing and taking turns are learned during this stage. Parents should model appropriate social interactions. Cooperative play should be encouraged to promote friendship among toddlers.
Early Childhood (3-6 years)

Image Source: pexels
Physical Development
Coordination and Balance
Children of age three to six show significant improvement in coordination and balance. Activities like running, jumping, and climbing become more coordinated. To improve overall, outdoor play should be encouraged by parents. Children who engage in structured activities such as dance or gymnastics would have better performance in physical activity.
Hand-Eye Coordination
Hand-eye coordination shows excellent development during early childhood. Children develop to master tasks requiring accurate movements. Examples include coloring shapes, using scissors, and completing puzzles. There are a variety of activities available to challenge the development of these skills. Tools such as crayons, safety scissors, and building blocks can be provided for practice by parents.
Cognitive Development
Pre-Operational Thinking
Pre-operational thinking describes the cognitive development of three- to six-year-old children. In the stage initially defined by Jean Piaget, this period consists of symbolic thought and egocentrism. Children start using language to question and understand their world. Cognitive development is well nurtured by imaginative play. Simple games and storytelling can elicit pre-operational thinking.
Early Literacy and Numeracy
Early literacy and numeracy skills begin to develop in this period. The child becomes able to recognize the letters of the alphabet and numbers. It is important to develop the habit of reading every day to promote a liking for books and learning new words. Counting objects during play helps introduce simple math concepts. Educational toys and games can also support literacy and numeracy development.
Social and Emotional Development
Peer Relationships
Peer relationships become more important during early childhood. Children learn how to share, cooperate, and resolve conflicts. Playdates and group activities are ways children are given opportunities for social interaction. Parents and educators should model appropriate social behaviors. Promoting empathy and understanding helps the child develop strong peer relationships.
Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation develops significantly between three and six. Children are taught to recognize and manage their emotions. Techniques include deep breathing, or even counting, in order to regulate strong feelings. Parents teach children that all feelings are valid and help them practice appropriate expression. Routines and expectations also help with emotional regulation.
Key Findings: Parents and teachers play a significant role in the cognitive, social, and emotional development of a child in various ways and during daily routines.
Middle Childhood (6-12 years)
Physical Development
Growth Spurts
Between 6-12 years kids are likely to have some growth spurts or physical changes. During this period, children generally grow an average of 2.5 inches per year. The child’s weight is likely to increase at approximately 4 to 7 pounds per year. These changes denote important physical development. Parents must pay attention to these growth patterns to ensure that there is proper development.
Physical Fitness
Physical fitness takes on an ever-growing importance in middle childhood. Regular exercise provides for the proper growth and development of the muscles and heart. Exercises that promote physical fitness include running, swimming, and many team sports. Encourage participation in physical activities that help maintain fitness for a lifetime. Schools and communities often offer several programs to aid in the fitness of children.
Cognitive Development
Concrete Operational Thinking
It is concrete operational thinking that characterizes cognitive development during middle childhood. As described by Jean Piaget, children of this age group learn to logically reason about concrete events and happenings. Children learn to conserve and reverse principles taught. There is an extensive growth of problem-solving abilities as they learn to use logical thinking to solve everyday problems. In schools, students are presented with problems that enhance problem-solving skills.
Academic Skills
The academic skills of children show rapid development between the ages of 6 and 12. Reading becomes more proficient, with children being able to understand more complex texts. Math skills develop as children learn to perform operations with larger numbers. Science and social studies introduce new concepts and require children to think more critically. Teachers and parents are very important in providing advanced academic learning through both structured learning and enrichment activities.
Social and Emotional Development
Self-Concept
Self-concept becomes more concrete in middle childhood. Children begin to develop a much clearer sense of identity. Comparisons with peers help to determine self-esteem and self-worth. Positive reinforcement from parents and teachers will aid in creating a positive self-concept. Encouragement in developing interests and hobbies will aid in a definite sense of individualism.
Peer Influence
Peer influence becomes stronger between the ages of 6 and 12. Friendships become more meaningful and complicated. Kids learn to negotiate social interactions and empathize with others. Friends offer opportunities to practice social skills. Parents should help children create positive relationships and resist negative peer pressure. Open communications about friendships nurture emotional health.
Key Findings: The American Academy of Pediatrics states that a pediatrician should regularly check a child for growth patterns. These are used to determine if the child is growing normally or abnormally compared to their peers.
Adolescence (12-18 years)
Physical Development
Puberty
Puberty is the phase in physical development. Hormones activate the growth spurt and bring about secondary sexual characteristics. Puberty usually starts between the ages of 8 and 13 in girls and between 9 and 14 in boys. Girls go through breast development and their first menstruation; for boys, it is voice changes and muscle growth. Individual variations in all these respects are considerable. All of this is monitored by the family pediatrician through regularly scheduled examinations.
Physical Maturity
Physical maturity is the point at which growth stops and physical changes become fewer and less significant. By the end of adolescence, most people have achieved adult height and weight. Bone density continues to improve and muscle growth is ongoing. All of this with the supporting cast of a well-balanced diet and physical exercise. Parents should instill lifetime healthy habits in their teens.
Cognitive Development
Abstract Thinking
Abstract thinking is an important cognitive milestone of adolescence, typical for this stage in human development. This stage allows the child to think about abstract ideas and concepts not tied to directly observed, concrete experiences. Adolescents can now comprehend a hypothetical situation and complex thoughts. The ability to solve problems also increases, as does logical reasoning. Educational games that encourage abstract thinking stimulate cognitive development.
Decision Making
The potential to make decisions becomes far more significant in adolescence. As the prefrontal cortex matures, the ability to plan and weigh different possibilities ahead of time becomes more developed. Adolescents begin to make relatively more independent decisions on issues relating to education, relationships, and future aspirations. The provision of opportunities for responsible decision-making and encouraging critical thinking speeds this process. Guidance from parents and educators is very essential in the realization of this end.
Social and Emotional Development
Identity Formation
Identity formation represents a critical characteristic of social and Emotional Development in adolescence. Adolescents are looking for the roles and beliefs to build their sense of self. The most important influence on this course will be their peer relations and social interactions. In fact, the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry has found that wrestling with the meaning of social situations predicts stronger identity development and life satisfaction. This important phase in life is critical and must be guided through the most recommended way of self-exploration encouraged and a supportive environment facilitated..
Emotional Independence
This is the ability to take charge of one’s emotions and decisions in a relatively self-reliant manner. Teens become accustomed to handling their emotions and may develop ways to deal with stress. Emotional independence fosters maturity and resilience. Parents should be supportive yet give the adolescent breathing space. On their part, consistent support and open communication contribute toward emotional growth.
Key Findings: Scientists from the University of Southern California Rossier School of Education’s Center for Affective Neuroscience, Development, Learning, and Education have shown that adolescents who struggle with more profound meaning in social interactions ultimately experience greater brain growth, resulting in more adaptive identity development and increased life satisfaction over the years.
Growth Rate in Children
Understanding Growth Rate in Children
Monitoring Growth Patterns
Tracking growth patterns helps guarantee healthy development in children. Height and weight should be taken at regular intervals. Parents should maintain the data of these values accordingly. Pediatricians should compare the growth in height and weight with children’s peer groups. They often do this by using standard growth charts. All variations from the normal and expected growth are established with these charts. Growth problems will be detected at early stages if proper growth is not recorded with respect to time.
Role of Pediatricians
Pediatricians are responsible for the assessment of growth rates. Regular visits will help doctors measure and monitor physical development. Pediatricians monitor the growth patterns and provide advice to maintain proper growth. They also identify emerging health problems that can inhibit growth. Parents should therefore follow any advice given by pediatricians in matters regarding diet, exercise, and sleep. Regular medical checkups ensure that children attain their best growth.
Factors Influencing Growth Rate
Genetics
Genetics play a very vital role in the rate of growth among children. Several hereditary factors contribute to determining the potential height and body of a child. Many times, the height of a parent will assist in predicting the stature of a child. Genetic predispositions are also responsible for the period of growth bursts. So, all this genetic knowledge has set a kind of expectation about growing; still, genetics alone doesn’t determine the growth process.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
Nutrition and lifestyle play a significant role in fast-growing children. A balanced diet consists of all kinds of nutrients that are helpful in the physical development of an individual. Proteins, vitamins, and minerals are needed for muscle and bone development. Regular physical activity is encouraged for a sound body. Adequate sleep is also required for the secretion of growth hormones. Parents should encourage a healthy, balanced diet for the kids while also motivating them to live an active life. These are other things that result in optimal growth as well as the development of the child.
Survey Results: Six out of 10 US parents were identified in a survey where they are concerned that their babies are not reaching developmental milestones with regard to the knowledge and ability to monitor the rates of growth in children. Support and encouragement of development along the set milestones remains to be very vital during the development and growth of the children. Parents and other caregivers need to be knowledgeable and engaged concerning development in children. Following development regularly and intervening as early as possible will help children achieve their full potential. There are costless materials available from the CDC that may provide further assistance. Healthy growth lays the foundation for lifelong health and well-being.
Health And Fitness
Walgreens Closing 1,200 Stores: A Major Shift in U.S. Retail Pharmacy

Walgreens has announced plans to close 1,200 stores across the U.S. by 2027 in an effort to optimize its operations. This decision comes after facing profitability challenges, increased competition, and market shifts. CEO Tim Wentworth cited underperforming locations and a difficult consumer environment as primary reasons for the closures. The company aims to focus on its core retail pharmacy business while cutting costs and improving long-term growth potential.
Why Is Walgreens Closing Stores?
Walgreens faces multiple challenges, including shrinking profit margins and decreased foot traffic. In response to inflation and lower consumer spending, the company is streamlining operations by targeting underperforming locations for closure. The ongoing shift to online pharmacies and the rise of competitors like CVS have also put pressure on Walgreens’ brick-and-mortar stores.
Impact on Customers and Communities
Many customers worry about losing access to convenient pharmacy services, especially in smaller communities. However, Walgreens aims to maintain robust service levels by focusing on profitable stores and enhancing its digital offerings. The closures could create opportunities for local pharmacies to fill the gap left by Walgreens in certain areas, though concerns remain about the broader impact on healthcare access.
What’s Next for Walgreens?
Walgreens is not just shutting stores but also revamping its business strategy. The company is reducing its stake in VillageMD and refocusing on pharmacy operations. Walgreens is not just closing stores; the company is also implementing a major shift in its business strategy. This includes reducing its stake in VillageMD and refocusing on its pharmacy operations.
The company will continue to offer retail health services, but with a leaner footprint and improved operational efficiency. As these changes unfold, consumers may see further shifts in how and where they receive pharmacy services. The company’s strategic shift is a response to a changing retail landscape and the need to adapt to changing consumer preferences. Walgreens is making a significant investment in its pharmacy operations to ensure that it can provide the best possible pharmacy care for its customers.
Most Searched Queries Regarding Walgreens Closures:
- “Why is Walgreens closing stores?”
- “List of Walgreens stores closing”
- “Impact of Walgreens closures on healthcare”
- “Alternatives to Walgreens pharmacy services”
Walgreens’ future will depend on how well it adapts to changing consumer preferences and a highly competitive retail landscape.
Financial Struggles & Reduced Profitability
Walgreens has been struggling with reduced profit margins due to inflation, higher shrink (inventory losses from theft and errors), and declining foot traffic. The ongoing changes in the retail pharmacy landscape have prompted Walgreens to reevaluate its operations and shutter underperforming stores. This decision is part of a larger effort to cut costs, streamline its footprint, and optimize the company’s future profitability.
The company is also seeking to improve its ability to compete with other retail pharmacies, such as CVS Health and Rite Aid. Walgreens is also looking to improve its ability to compete with online retailers like Amazon, which have been expanding their healthcare offerings. The decision is also part of a larger effort to cut costs, streamline its footprint, and optimize the company’s future profitability.
Impact on Stock Performance
Walgreens’ financial challenges have caused its shares to drop significantly—over 45% in the last year. In response, the company also lowered its profit forecast for fiscal year 2024 to between $2.80 and $2.95 per share, down from the previous estimate of $3.20 to $3.35 per share.
Customer Service Adjustments
Though the store closures will reduce Walgreens’ physical presence, the company plans to enhance its digital services. It is also reworking its health services, including retail health clinics and pharmacy services, to focus on high-performing regions. Walgreens is reducing its involvement in secondary ventures, like VillageMD, to realign with its core retail pharmacy business.
Workforce Reductions
As part of its cost-cutting strategy, Walgreens recently announced that it will be closing 1,200 stores by 2027. The company also revealed that it will be reducing its workforce, including layoffs across its corporate and retail divisions. While the exact number of job cuts has not been specified, the company has stated that it will be making the necessary changes to ensure its long-term success. This includes layoffs across its corporate and retail divisions, though the company has not specified the exact number of job cuts.
Questions from Consumers
- “How many Walgreens stores are closing?”
- “What will happen to Walgreens employees?”
- “Will Walgreens’ pharmacy services be affected by store closures?”
- “Are there alternatives to Walgreens in my area?”
The closures are part of Walgreens’ strategy to address the rapidly changing retail pharmacy market, ensuring long-term growth while navigating current economic challenges.
FAQs on Walgreens’ Store Closures
1. How many Walgreens stores are closing?
Walgreens plans to close around 1,200 stores by 2027, primarily focusing on underperforming locations.
2. Why is Walgreens closing stores?
Walgreens is closing stores due to declining profit margins, high operational costs, inflationary pressures, and competition from other pharmacies and online retailers.
3. Will pharmacy services be impacted?
While some stores will close, Walgreens intends to enhance its digital pharmacy services to maintain customer access to prescriptions.
4. What will happen to Walgreens employees?
Layoffs are expected as a result of these closures, but the company has not specified the total number of jobs affected.
5. How will this impact local communities?
Closures could lead to reduced access to pharmacy services in certain areas, particularly smaller communities, but Walgreens is working to consolidate operations to maintain essential services.
6. How do I find out if my local Walgreens is closing?
The company will release specific lists of store closures over time, so keep an eye on official announcements or check with your local store.
7. Are there alternatives to Walgreens?
Customers can explore other national chains like CVS, Rite Aid, or local pharmacies, depending on location and services offered.
Health And Fitness
How to Choose a Rehab for Lasting Recovery

Choosing the right rehabilitation center can be one of the most transformative decisions in your journey to sobriety. It’s more than just picking a place—it’s about finding the support system that will walk with you toward lasting recovery and a better quality of life. Did you know that 80% of patients report improved health after completing their programs? With the right rehab center, your chances of staying drug-free after treatment rise to as much as 95%.
The path to recovery is deeply personal, and the rehab center you choose can play a pivotal role in shaping your future. This decision can be the key to unlocking a healthier, happier life. You deserve the best care, so take the time to make an informed choice that will support your long-term success.
Identifying Personal Treatment Goals
Assessing Your Needs
Defining your personal treatment goals helps you focus on what truly matters in your recovery journey. What do you want to achieve? Is it maintaining sobriety, improving your mental health, or rebuilding relationships? By being clear about your goals, you can choose a rehab center that aligns with your vision for a better future.
It’s also important to understand the level of care you need. Some people may thrive in an intensive inpatient program, while others find success in outpatient care. Take a moment to honestly assess your situation. The right support can make all the difference, guiding you toward lasting recovery and a life full of possibility.
Consulting with Treatment Providers
Health And Fitness
Boost Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes

How to Boost Muscle Power: Top Workouts for Athletes
Muscle power is crucial for athletic performance, as athletes depend on generating power rather than solely focusing on maximum strength. Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes are designed to enhance power output, which is a key predictor of success in various sports and also aids in improving mobility among older adults. These workouts are essential for health and fitness, as they focus on exercises that increase explosive strength, tailoring muscles for specific sports. By engaging in these targeted training sessions, athletes can achieve peak performance.
Definition and Importance
What is Muscle Power?
Muscle power refers to the ability of muscles to exert force rapidly. This concept combines strength and speed to produce explosive movements. Athletes rely on muscle power to perform actions like jumping, sprinting, and throwing. The relationship between strength and speed defines muscle power. Training programs often focus on enhancing this attribute to improve athletic performance.
Why is it crucial for athletes?
Athletes benefit from increased muscle power in several ways. Enhanced muscle power contributes to better performance in sports-specific tasks. Activities such as sprinting, jumping, and changing direction quickly require high levels of muscle power. Greater muscle power also reduces the risk of injury by improving the body’s ability to handle dynamic movements. According to research, muscular strength and power significantly influence athletic performance, impacting speed, endurance, and resilience.
Factors Affecting Muscle Power
Muscle Fiber Types
Muscle fibers play a crucial role in determining muscle power. There are two main types of muscle fibers: Type I (slow-twitch) and Type II (fast-twitch). Fast-twitch fibers generate more power and are essential for explosive movements. Athletes with a higher proportion of fast-twitch fibers tend to excel in power-based activities. Training can enhance the efficiency of these fibers, leading to improved performance.
Neuromuscular Efficiency
Neuromuscular efficiency refers to the ability of the nervous system to communicate effectively with muscles. Efficient neuromuscular function allows for quicker and more powerful muscle contractions. Athletes can improve neuromuscular efficiency through specific training techniques. Exercises that emphasize speed and coordination help enhance this connection. Improved neuromuscular efficiency results in better force production and overall athletic performance.
Muscle Power Training for Beginners: Improve Flexibility and Mobility
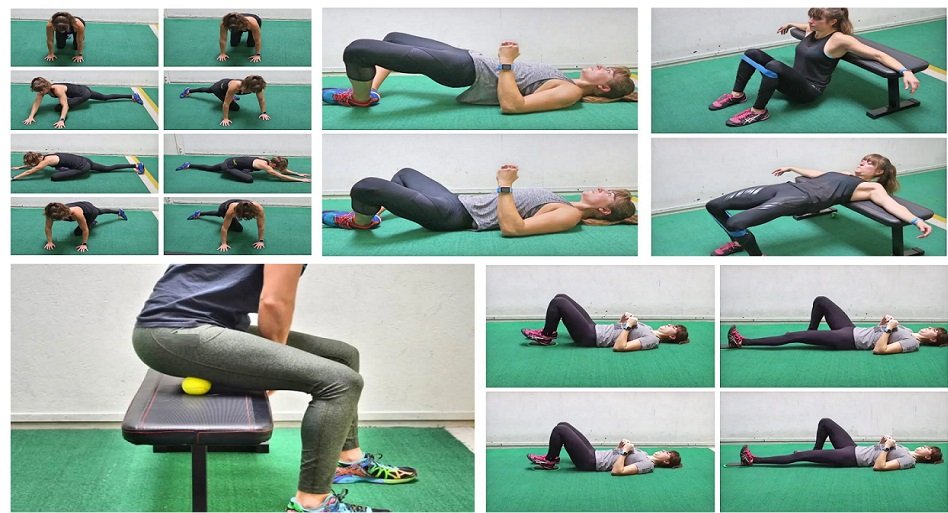

Flexibility is a crucial component of physical fitness, but for many people, tightness and stiffness in the body can make stretching uncomfortable or intimidating. If you’re not very flexible, this 8-minute stretching routine is designed for you. It’s simple, requires no equipment, and addresses all the major muscle groups to help improve your mobility. Say goodbye to complicated yoga poses and advanced stretches—this is all about practical movements that will gently loosen up your muscles and joints.
1. Lumbar Rotation Stretch
This stretch targets the lower back and hips, two areas where many people experience tightness.
How to Do It:
- Lie on your back with your right knee bent.
- Use your left hand to grab the outside of your right knee and gently pull it over to your left side, allowing your body to twist.
- You should feel a stretch through your lower back and hip.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds.
Tip: Keep your movements slow and controlled, and only twist as far as is comfortable for your body.
2. Supine Hamstring Stretch
Hamstrings are often one of the tightest muscle groups, especially if you sit for long periods.
How to Do It:
- Lie on your back with your left leg straight.
- Cup both hands behind your right knee.
- Slowly straighten your right leg toward the ceiling until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh (hamstring).
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch legs.
Tip: Be sure not to force your leg straight; aim for a gentle stretch without pain.
3. Piriformis Stretch
The piriformis is a small muscle deep in the hip that can cause discomfort when tight. This stretch can relieve tension in the hips and lower back.
How to Do It:
- Cross your right leg over your left knee, forming a “figure four.”
- Grab your left knee and pull it toward your chest until you feel a stretch in your right hip.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: This is an excellent stretch for reducing tightness that contributes to sciatica or hip discomfort.
4. Tall Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
Your hip flexors can get tight from sitting too much, which can affect your posture and mobility. This stretch helps to lengthen those muscles.
How to Do It:
- Kneel on your right knee and take a large step forward with your left foot.
- Shift your weight forward, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in the front of your right hip.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Keep your torso upright and avoid arching your lower back.
5. Kneeling Hamstring Stretch
This is another great stretch for your hamstrings, but from a kneeling position.
How to Do It:
- From the tall kneeling position, shift your weight back onto your right knee.
- Straighten your left leg in front of you.
- Keep your back straight and lean forward from the hips until you feel a stretch in your left hamstring.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Engage your core to avoid rounding your back during this stretch.
6. Seated Spine Rotation Stretch
Spinal mobility is essential for everyday movements like bending and twisting. This stretch helps to loosen up your mid and upper back.
How to Do It:
- Sit with your legs out in front of you.
- Cross your left leg over your right, planting your left foot flat on the floor.
- Twist your torso to the left, placing your right elbow on the outside of your left knee for leverage.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: This stretch may cause a few pops in your back, but that’s perfectly normal as long as there’s no pain.
7. Child’s Pose Stretch
The child’s pose is a classic yoga stretch that targets the entire back, especially the lats and spine.
How to Do It:
- Start on all fours (hands and knees).
- Sit your hips back toward your heels while reaching your arms forward.
- Tuck your chin into your chest and sink into the stretch, feeling the lengthening in your back.
- Hold for 30 seconds.
Tip: Breathe deeply and let your body relax into the stretch for maximum benefit.
8. Upper Back Extension
This movement opens up the chest and stretches the upper back, perfect for counteracting poor posture from sitting.
How to Do It:
- Sit or stand with your fingertips behind your head.
- Bring your elbows together and fold forward slightly.
- Then, lift your chest and elbows up, opening through your upper back and chest.
- Repeat this movement three times.
Tip: This dynamic stretch is excellent for improving posture and chest mobility.
9. Upper Traps Stretch
The trapezius muscles in the neck and upper back can get very tight, especially if you spend a lot of time hunched over a computer or phone.
How to Do It:
- Tilt your head to the left, bringing your left ear toward your left shoulder.
- Use your left hand to gently apply pressure to the right side of your head.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Keep the stretch gentle—this is a sensitive area, and too much pressure can cause discomfort.
Plyometric Exercises
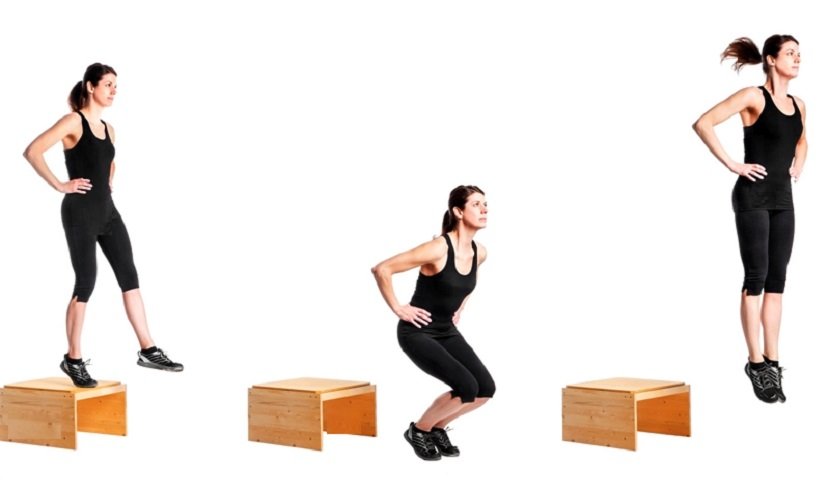

Box Jumps
Box jumps enhance explosive power. Athletes use box jumps to improve vertical leap and agility. The exercise involves jumping onto a raised platform. Box jumps require coordination and strength. Consistent practice increases muscle power and reduces injury risk.
Depth Jumps
Depth jumps focus on rapid force production. Athletes step off a box and immediately jump upon landing. This exercise trains muscles to react quickly. Depth jumps improve neuromuscular efficiency. Athletes gain better performance in sports requiring quick direction changes.
Olympic Weightlifting
Clean and Jerk
The clean and jerk builds total body power. Athletes lift a barbell from the ground to overhead. This movement combines strength and speed. The clean and jerk enhances muscle power and coordination. Regular training improves athletic performance in explosive sports.
Snatch
The snatch develops explosive strength. Athletes lift a barbell from the ground to overhead in one motion. This exercise requires precision and power. The snatch increases muscle power and flexibility. Athletes benefit from improved performance in dynamic sports activities.
Sprint Training
Short Distance Sprints
Short distance sprints boost speed and power. Athletes run at maximum effort for short distances. This training enhances fast-twitch muscle fibers. Short sprints improve acceleration and agility. Athletes gain an edge in sports demanding quick bursts of speed.
Hill Sprints
Hill sprints increase lower body strength. Athletes sprint uphill to build muscle power. This exercise challenges endurance and explosiveness. Hill sprints improve cardiovascular fitness and leg strength. Athletes experience enhanced performance in endurance-based sports.
Case Studies show that integrating these Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes leads to significant improvements. Research highlights the effectiveness of combining strength and ballistic-power training. Athletes achieve better results through targeted programs. These workouts reduce injuries and enhance overall performance.
Programming Ideas for Power Development
Periodization Techniques
Linear Periodization
Linear periodization involves a structured progression in training intensity. Athletes start with high-volume, low-intensity workouts. Over time, the focus shifts to low-volume, high-intensity sessions. This method enhances muscle power by gradually increasing the load on muscles. Research shows that linear periodization can lead to significant strength gains. Coaches often use this technique to prepare athletes for peak performance during competitions.
Undulating Periodization
Undulating periodization offers more variation in training. Athletes alternate between different intensities and volumes within a week. This approach prevents training plateaus and keeps workouts engaging. Studies indicate that undulating periodization can produce similar strength gains as linear models. Athletes benefit from the flexibility and adaptability of this method. Coaches can tailor programs to meet specific needs and goals.
Integrating Power Workouts into Training
Weekly Training Schedule
A well-structured weekly training schedule maximizes power development. Athletes should include a mix of strength, speed, and endurance sessions. Each week might feature two to three power-focused workouts. These sessions could involve plyometrics, Olympic lifts, or sprint drills. Rest days are crucial for recovery and muscle growth. Monitoring progress helps in adjusting the schedule for optimal results.
Balancing Power and Endurance
Balancing power and endurance is essential for comprehensive athletic performance. Athletes should incorporate both elements into their training regimen. Power workouts enhance explosive strength and speed. Endurance sessions build stamina and cardiovascular health. A balanced approach ensures athletes maintain peak performance across various sports demands. Coaches can design programs that integrate both aspects effectively.
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoKolkata Doctor Case: Tragic Story of Dr. Moumita Debnath
-

 Health And Fitness1 year ago
Health And Fitness1 year agoPepsi Zero Sugar vs Diet Pepsi: Which Is Healthier?
-

 Health And Fitness1 year ago
Health And Fitness1 year agoHow to Choose a Rehab for Lasting Recovery
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoLondon King Opens Up About Her Relationship with Rob Schneider
-

 Tech Innovation1 year ago
Tech Innovation1 year agoTop Machine Learning and Deep Learning Trends for 2024
-

 Tech Innovation1 year ago
Tech Innovation1 year agoHuawei Mate XT: A Detailed Review of the World’s First Tri-Fold Smartphone
-

 Health And Fitness1 year ago
Health And Fitness1 year agoCoca-Cola Zero Sugar vs Diet Coke: Which One to Choose In 2025?
-

 News11 months ago
News11 months agoTyra Banks Biography: Age, Husband, Net Worth