Health And Fitness
Understanding Diabetes and Its Causes

Image Source: pexels
What is Diabetes?
Definition and Types
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body fails to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. The main types of diabetes include Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and Gestational Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type usually appears in children and young adults. Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes need daily insulin injections to manage their condition. Without insulin, blood sugar levels rise dangerously high, leading to severe health complications.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes develops when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot use insulin effectively. This condition often results from a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle choices such as poor diet and lack of exercise. Over time, high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the circulatory, nervous, and immune systems.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. However, individuals who experience gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes later in life. This condition can lead to complications such as high blood pressure during pregnancy and increased birth weight of the newborn.
How Diabetes Affects the Body
Blood Sugar Regulation
The body regulates blood sugar levels through the hormone insulin. Insulin allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream for energy. In diabetes, this regulation process malfunctions, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Prolonged high blood sugar can damage organs and tissues.
Insulin Function
Insulin plays a crucial role in maintaining normal blood sugar levels. In Type 1 Diabetes, the body produces little or no insulin. In Type 2 Diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. Both scenarios result in high blood sugar levels, which require medical intervention to manage.
Symptoms of Diabetes

Image Source: pexels
Common Symptoms
Increased Thirst
Increased thirst, also known as polydipsia, often serves as an early indicator of diabetes. Elevated blood sugar levels cause the body to pull fluid from tissues, leading to dehydration. This dehydration triggers a persistent feeling of thirst.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination, or polyuria, occurs when excess glucose in the blood forces the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb it. When the kidneys cannot keep up, the excess glucose is excreted into the urine, drawing fluids from the body and causing frequent urination.
Extreme Fatigue
Extreme fatigue results from the body’s inability to use glucose for energy effectively. Insufficient insulin or insulin resistance prevents cells from absorbing glucose, leading to a lack of energy and persistent tiredness.
Symptoms Specific to Type 1 and Type 2
Type 1 Symptoms
Type 1 diabetes symptoms often appear suddenly and can include unintended weight loss, increased hunger, and irritability. The immune system attacks insulin-producing cells, leading to a rapid onset of symptoms. Immediate medical attention is crucial for managing Type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Symptoms
Type 2 diabetes symptoms develop more gradually and may include blurred vision, slow-healing sores, frequent infections, and numbness or tingling in the hands or feet. These symptoms result from prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging various body systems. Early detection and lifestyle changes can help manage Type 2 diabetes effectively.
Causes of Diabetes
Genetic Factors
Family History
Family history significantly impacts the likelihood of developing diabetes. Individuals with a close relative who has diabetes face a higher risk. Studies indicate that genetics play a crucial role in type 2 diabetes. Specific racial and ethnic groups show a higher prevalence due to genetic predispositions.
Genetic Mutations
Genetic mutations also contribute to diabetes risk. Over 100 genetic variants have been linked to type 2 diabetes. These genetic variations interact with lifestyle factors, increasing the overall risk. Research highlights the importance of understanding these genetic components for better disease management.
Environmental Factors
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices greatly influence diabetes development. Poor diet and lack of exercise are major contributors. Consuming high-calorie, low-nutrient foods leads to weight gain and insulin resistance. Physical inactivity further exacerbates these issues, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise play pivotal roles in diabetes prevention and management. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing diabetes. Health And Fitness professionals recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Other Contributing Factors
Autoimmune Reactions
Autoimmune reactions primarily cause type 1 diabetes. The immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This destruction leads to insufficient insulin production, requiring lifelong insulin therapy. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing type 1 diabetes effectively.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes can also trigger diabetes. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and Cushing’s syndrome increase the risk. Hormonal imbalances affect insulin function, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Monitoring and managing these conditions help reduce the risk of diabetes.
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Medical Tests
Blood Glucose Tests
Doctors use blood glucose tests to measure the amount of sugar in the blood. These tests help diagnose diabetes and monitor its management. The most common blood glucose tests include fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and random plasma glucose (RPG).
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): Patients must fast for at least eight hours before this test. The test measures blood sugar levels after fasting. High levels indicate diabetes or prediabetes.
- Random Plasma Glucose (RPG): This test does not require fasting. Doctors use it to measure blood sugar levels at any time of the day. Elevated levels suggest diabetes.
A1C Test
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test, provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. This test measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
- A1C Levels:
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Studies show that maintaining A1C levels below 7% reduces the risk of complications in people with diabetes.
Diagnostic Criteria
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting blood sugar levels play a crucial role in diagnosing diabetes. Doctors use specific criteria to interpret these levels:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests
Accurate measurement of fasting blood sugar levels helps identify individuals at risk and those who need immediate intervention.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) assesses how the body processes sugar. This test involves several steps:
- Patients fast for at least eight hours.
- Doctors measure fasting blood sugar levels.
- Patients drink a sugary solution.
- Doctors measure blood sugar levels at intervals, usually after two hours.
- OGTT Results:
- Normal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 140 to 199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
The OGTT helps diagnose diabetes and prediabetes, providing valuable information for early intervention.
Treatment and Management

Image Source: unsplash
Medication
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy remains essential for managing Type 1 diabetes and some cases of Type 2 diabetes. Health professionals administer insulin through injections or insulin pumps. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells, providing energy. Different types of insulin include rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. Each type has a specific onset, peak, and duration of action. Proper insulin management reduces the risk of complications.
Oral Medications
Oral medications play a crucial role in managing Type 2 diabetes. These medications help control blood sugar levels through various mechanisms. Some drugs increase insulin production, while others enhance insulin sensitivity or reduce glucose absorption. Common oral medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors. Doctors tailor medication plans based on individual needs and health conditions.
Lifestyle Changes
Diet Modifications
Diet modifications significantly impact diabetes management. A balanced diet helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Health And Fitness experts recommend consuming whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. The DPP trial emphasized individualized dietary approaches, such as Mediterranean-style, plant-based, or DASH diets. Reducing calorie intake and avoiding high-sugar foods can prevent blood sugar spikes. Consistent dietary changes support long-term diabetes control.
Exercise Routines
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps manage diabetes. Health professionals suggest at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling enhance cardiovascular health and aid weight management. Exercise routines should be tailored to individual fitness levels and preferences. Consistent physical activity reduces the risk of diabetes complications and supports overall well-being.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are vital for effective diabetes management. Healthcare providers monitor blood sugar levels, assess treatment efficacy, and adjust medication plans. Routine visits help detect early signs of complications, enabling timely intervention. Patients should schedule check-ups every three to six months, depending on their condition’s severity. Consistent medical supervision ensures optimal diabetes control.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to track their glucose levels and make informed decisions about their treatment. Patients use glucometers to measure blood sugar at home. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide real-time data, offering insights into blood sugar trends. Regular monitoring helps identify patterns and adjust lifestyle choices accordingly. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels reduces the risk of complications.
Prevention of Diabetes
Risk Factor Management
Healthy Eating
Healthy eating plays a crucial role in preventing diabetes. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Consuming foods with a low glycemic index reduces the risk of blood sugar spikes. Health And Fitness experts recommend limiting the intake of sugary beverages and processed foods. Incorporating fiber-rich foods aids in digestion and promotes satiety, reducing overeating.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity significantly lowers the risk of developing diabetes. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week improves insulin sensitivity. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling enhance cardiovascular health. Exercise also aids in weight management, which is critical for diabetes prevention. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Lifestyle Change Program demonstrated that participants reduced their chances of developing type 2 diabetes by 58 percent through lifestyle changes.
Early Detection
Screening Tests
Screening tests are essential for early detection of diabetes. Doctors use fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and A1C tests to identify individuals at risk. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, preventing complications. Regular screening is especially important for individuals with a family history of diabetes or other risk factors. The Greater Richmond Diabetes Control Program showed that early detection and management improve health outcomes.
Awareness of Symptoms
Awareness of symptoms is vital for early detection of diabetes. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and extreme fatigue. Recognizing these signs prompts individuals to seek medical advice. Early intervention can prevent the progression of diabetes and its complications. Health And Fitness professionals emphasize the importance of educating the public about diabetes symptoms.
Complications of Diabetes
Short-term Complications
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop below normal. This condition can result from excessive insulin or certain diabetes medications. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and dizziness. Severe hypoglycemia may lead to seizures or unconsciousness. Immediate treatment with fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, helps restore normal blood sugar levels.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication primarily affecting individuals with Type 1 diabetes. It occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This condition results from insufficient insulin, causing the body to break down fat for energy. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid breathing. DKA requires urgent medical attention to prevent life-threatening outcomes.
Long-term Complications
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a major long-term complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves in the heart. This increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Managing blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure levels reduces cardiovascular risks. Regular exercise and a heart-healthy diet also contribute to prevention.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy refers to nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. This condition affects various parts of the body, including the hands and feet. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, and pain. Severe cases may lead to loss of sensation, increasing the risk of injuries and infections. Controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle help manage neuropathy.
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye complication that can lead to vision loss. High blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. Early stages may not show symptoms, but advanced stages cause blurred vision and blindness. Regular eye exams and blood sugar control are essential for preventing retinopathy. Treatment options include laser therapy and medication injections.
Living with Diabetes
Daily Management
Meal Planning
Effective meal planning plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. A balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Health And Fitness experts recommend consuming whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control is essential to avoid blood sugar spikes. Consistent meal timing aids in better glucose regulation. Avoiding sugary beverages and processed foods reduces the risk of complications. Consulting a registered dietitian can provide personalized meal plans.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and supports diabetes management. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week improves overall health. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling boost cardiovascular health. Exercise routines should match individual fitness levels and preferences. Consistent physical activity helps control weight and reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications. Monitoring blood sugar levels before and after exercise ensures safe practices.
Support Systems
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play an integral role in managing diabetes. Regular consultations help monitor blood sugar levels and adjust treatment plans. Endocrinologists specialize in diabetes care and provide expert guidance. Primary care physicians offer continuous support and manage overall health. Diabetes educators teach self-management skills and provide valuable resources. Routine check-ups ensure early detection of potential complications.
Support Groups
Support groups offer emotional and practical assistance for individuals living with diabetes. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges provides comfort and motivation. Support groups often include educational sessions led by Health And Fitness professionals. These sessions cover topics like meal planning, exercise routines, and stress management. Online forums and local community groups provide accessible support options. Engaging with support groups fosters a sense of community and encourages proactive health management.
Understanding diabetes and its causes is essential for effective management and prevention. Increased awareness can significantly improve health outcomes. Continuous education empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Managing blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels helps prevent complications. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial. Consulting healthcare providers for symptoms or concerns ensures proper guidance and support. Utilizing resources like the “Know Your Risk Tool” from Diabetes UK can aid in assessing risk factors and taking proactive steps.
Health And Fitness
Walgreens Closing 1,200 Stores: A Major Shift in U.S. Retail Pharmacy

Walgreens has announced plans to close 1,200 stores across the U.S. by 2027 in an effort to optimize its operations. This decision comes after facing profitability challenges, increased competition, and market shifts. CEO Tim Wentworth cited underperforming locations and a difficult consumer environment as primary reasons for the closures. The company aims to focus on its core retail pharmacy business while cutting costs and improving long-term growth potential.
Why Is Walgreens Closing Stores?
Walgreens faces multiple challenges, including shrinking profit margins and decreased foot traffic. In response to inflation and lower consumer spending, the company is streamlining operations by targeting underperforming locations for closure. The ongoing shift to online pharmacies and the rise of competitors like CVS have also put pressure on Walgreens’ brick-and-mortar stores.
Impact on Customers and Communities
Many customers worry about losing access to convenient pharmacy services, especially in smaller communities. However, Walgreens aims to maintain robust service levels by focusing on profitable stores and enhancing its digital offerings. The closures could create opportunities for local pharmacies to fill the gap left by Walgreens in certain areas, though concerns remain about the broader impact on healthcare access.
What’s Next for Walgreens?
Walgreens is not just shutting stores but also revamping its business strategy. The company is reducing its stake in VillageMD and refocusing on pharmacy operations. Walgreens is not just closing stores; the company is also implementing a major shift in its business strategy. This includes reducing its stake in VillageMD and refocusing on its pharmacy operations.
The company will continue to offer retail health services, but with a leaner footprint and improved operational efficiency. As these changes unfold, consumers may see further shifts in how and where they receive pharmacy services. The company’s strategic shift is a response to a changing retail landscape and the need to adapt to changing consumer preferences. Walgreens is making a significant investment in its pharmacy operations to ensure that it can provide the best possible pharmacy care for its customers.
Most Searched Queries Regarding Walgreens Closures:
- “Why is Walgreens closing stores?”
- “List of Walgreens stores closing”
- “Impact of Walgreens closures on healthcare”
- “Alternatives to Walgreens pharmacy services”
Walgreens’ future will depend on how well it adapts to changing consumer preferences and a highly competitive retail landscape.
Financial Struggles & Reduced Profitability
Walgreens has been struggling with reduced profit margins due to inflation, higher shrink (inventory losses from theft and errors), and declining foot traffic. The ongoing changes in the retail pharmacy landscape have prompted Walgreens to reevaluate its operations and shutter underperforming stores. This decision is part of a larger effort to cut costs, streamline its footprint, and optimize the company’s future profitability.
The company is also seeking to improve its ability to compete with other retail pharmacies, such as CVS Health and Rite Aid. Walgreens is also looking to improve its ability to compete with online retailers like Amazon, which have been expanding their healthcare offerings. The decision is also part of a larger effort to cut costs, streamline its footprint, and optimize the company’s future profitability.
Impact on Stock Performance
Walgreens’ financial challenges have caused its shares to drop significantly—over 45% in the last year. In response, the company also lowered its profit forecast for fiscal year 2024 to between $2.80 and $2.95 per share, down from the previous estimate of $3.20 to $3.35 per share.
Customer Service Adjustments
Though the store closures will reduce Walgreens’ physical presence, the company plans to enhance its digital services. It is also reworking its health services, including retail health clinics and pharmacy services, to focus on high-performing regions. Walgreens is reducing its involvement in secondary ventures, like VillageMD, to realign with its core retail pharmacy business.
Workforce Reductions
As part of its cost-cutting strategy, Walgreens recently announced that it will be closing 1,200 stores by 2027. The company also revealed that it will be reducing its workforce, including layoffs across its corporate and retail divisions. While the exact number of job cuts has not been specified, the company has stated that it will be making the necessary changes to ensure its long-term success. This includes layoffs across its corporate and retail divisions, though the company has not specified the exact number of job cuts.
Questions from Consumers
- “How many Walgreens stores are closing?”
- “What will happen to Walgreens employees?”
- “Will Walgreens’ pharmacy services be affected by store closures?”
- “Are there alternatives to Walgreens in my area?”
The closures are part of Walgreens’ strategy to address the rapidly changing retail pharmacy market, ensuring long-term growth while navigating current economic challenges.
FAQs on Walgreens’ Store Closures
1. How many Walgreens stores are closing?
Walgreens plans to close around 1,200 stores by 2027, primarily focusing on underperforming locations.
2. Why is Walgreens closing stores?
Walgreens is closing stores due to declining profit margins, high operational costs, inflationary pressures, and competition from other pharmacies and online retailers.
3. Will pharmacy services be impacted?
While some stores will close, Walgreens intends to enhance its digital pharmacy services to maintain customer access to prescriptions.
4. What will happen to Walgreens employees?
Layoffs are expected as a result of these closures, but the company has not specified the total number of jobs affected.
5. How will this impact local communities?
Closures could lead to reduced access to pharmacy services in certain areas, particularly smaller communities, but Walgreens is working to consolidate operations to maintain essential services.
6. How do I find out if my local Walgreens is closing?
The company will release specific lists of store closures over time, so keep an eye on official announcements or check with your local store.
7. Are there alternatives to Walgreens?
Customers can explore other national chains like CVS, Rite Aid, or local pharmacies, depending on location and services offered.
Health And Fitness
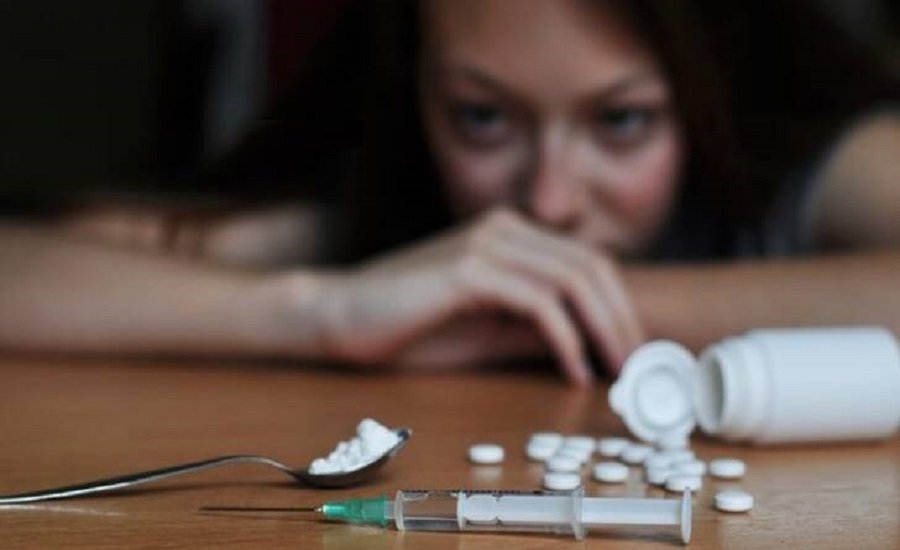
How to Choose a Rehab for Lasting Recovery

Choosing the right rehabilitation center can be one of the most transformative decisions in your journey to sobriety. It’s more than just picking a place—it’s about finding the support system that will walk with you toward lasting recovery and a better quality of life. Did you know that 80% of patients report improved health after completing their programs? With the right rehab center, your chances of staying drug-free after treatment rise to as much as 95%.
The path to recovery is deeply personal, and the rehab center you choose can play a pivotal role in shaping your future. This decision can be the key to unlocking a healthier, happier life. You deserve the best care, so take the time to make an informed choice that will support your long-term success.
Identifying Personal Treatment Goals
Assessing Your Needs
Defining your personal treatment goals helps you focus on what truly matters in your recovery journey. What do you want to achieve? Is it maintaining sobriety, improving your mental health, or rebuilding relationships? By being clear about your goals, you can choose a rehab center that aligns with your vision for a better future.
It’s also important to understand the level of care you need. Some people may thrive in an intensive inpatient program, while others find success in outpatient care. Take a moment to honestly assess your situation. The right support can make all the difference, guiding you toward lasting recovery and a life full of possibility.
Consulting with Treatment Providers
Health And Fitness
Boost Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes

How to Boost Muscle Power: Top Workouts for Athletes
Muscle power is crucial for athletic performance, as athletes depend on generating power rather than solely focusing on maximum strength. Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes are designed to enhance power output, which is a key predictor of success in various sports and also aids in improving mobility among older adults. These workouts are essential for health and fitness, as they focus on exercises that increase explosive strength, tailoring muscles for specific sports. By engaging in these targeted training sessions, athletes can achieve peak performance.
Definition and Importance
What is Muscle Power?
Muscle power refers to the ability of muscles to exert force rapidly. This concept combines strength and speed to produce explosive movements. Athletes rely on muscle power to perform actions like jumping, sprinting, and throwing. The relationship between strength and speed defines muscle power. Training programs often focus on enhancing this attribute to improve athletic performance.
Why is it crucial for athletes?
Athletes benefit from increased muscle power in several ways. Enhanced muscle power contributes to better performance in sports-specific tasks. Activities such as sprinting, jumping, and changing direction quickly require high levels of muscle power. Greater muscle power also reduces the risk of injury by improving the body’s ability to handle dynamic movements. According to research, muscular strength and power significantly influence athletic performance, impacting speed, endurance, and resilience.
Factors Affecting Muscle Power
Muscle Fiber Types
Muscle fibers play a crucial role in determining muscle power. There are two main types of muscle fibers: Type I (slow-twitch) and Type II (fast-twitch). Fast-twitch fibers generate more power and are essential for explosive movements. Athletes with a higher proportion of fast-twitch fibers tend to excel in power-based activities. Training can enhance the efficiency of these fibers, leading to improved performance.
Neuromuscular Efficiency
Neuromuscular efficiency refers to the ability of the nervous system to communicate effectively with muscles. Efficient neuromuscular function allows for quicker and more powerful muscle contractions. Athletes can improve neuromuscular efficiency through specific training techniques. Exercises that emphasize speed and coordination help enhance this connection. Improved neuromuscular efficiency results in better force production and overall athletic performance.
Muscle Power Training for Beginners: Improve Flexibility and Mobility
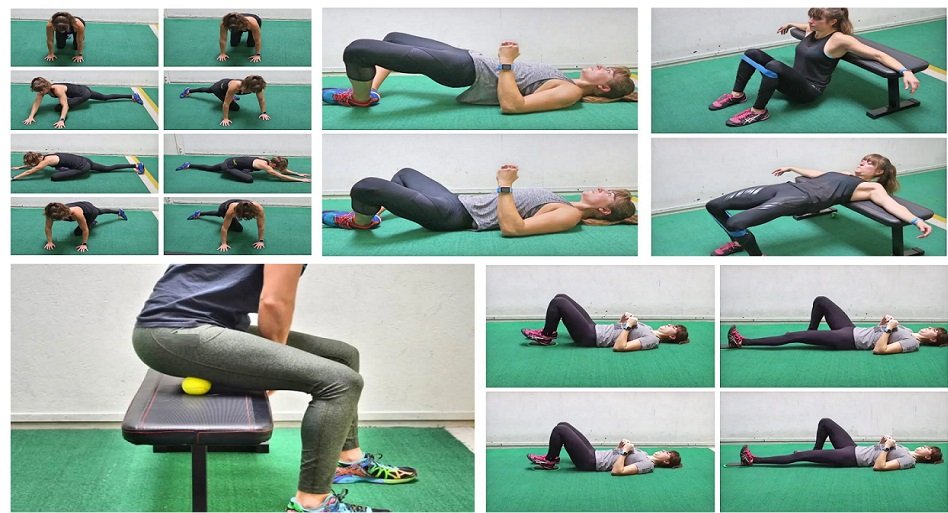

Flexibility is a crucial component of physical fitness, but for many people, tightness and stiffness in the body can make stretching uncomfortable or intimidating. If you’re not very flexible, this 8-minute stretching routine is designed for you. It’s simple, requires no equipment, and addresses all the major muscle groups to help improve your mobility. Say goodbye to complicated yoga poses and advanced stretches—this is all about practical movements that will gently loosen up your muscles and joints.
1. Lumbar Rotation Stretch
This stretch targets the lower back and hips, two areas where many people experience tightness.
How to Do It:
- Lie on your back with your right knee bent.
- Use your left hand to grab the outside of your right knee and gently pull it over to your left side, allowing your body to twist.
- You should feel a stretch through your lower back and hip.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds.
Tip: Keep your movements slow and controlled, and only twist as far as is comfortable for your body.
2. Supine Hamstring Stretch
Hamstrings are often one of the tightest muscle groups, especially if you sit for long periods.
How to Do It:
- Lie on your back with your left leg straight.
- Cup both hands behind your right knee.
- Slowly straighten your right leg toward the ceiling until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh (hamstring).
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch legs.
Tip: Be sure not to force your leg straight; aim for a gentle stretch without pain.
3. Piriformis Stretch
The piriformis is a small muscle deep in the hip that can cause discomfort when tight. This stretch can relieve tension in the hips and lower back.
How to Do It:
- Cross your right leg over your left knee, forming a “figure four.”
- Grab your left knee and pull it toward your chest until you feel a stretch in your right hip.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: This is an excellent stretch for reducing tightness that contributes to sciatica or hip discomfort.
4. Tall Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
Your hip flexors can get tight from sitting too much, which can affect your posture and mobility. This stretch helps to lengthen those muscles.
How to Do It:
- Kneel on your right knee and take a large step forward with your left foot.
- Shift your weight forward, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in the front of your right hip.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Keep your torso upright and avoid arching your lower back.
5. Kneeling Hamstring Stretch
This is another great stretch for your hamstrings, but from a kneeling position.
How to Do It:
- From the tall kneeling position, shift your weight back onto your right knee.
- Straighten your left leg in front of you.
- Keep your back straight and lean forward from the hips until you feel a stretch in your left hamstring.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Engage your core to avoid rounding your back during this stretch.
6. Seated Spine Rotation Stretch
Spinal mobility is essential for everyday movements like bending and twisting. This stretch helps to loosen up your mid and upper back.
How to Do It:
- Sit with your legs out in front of you.
- Cross your left leg over your right, planting your left foot flat on the floor.
- Twist your torso to the left, placing your right elbow on the outside of your left knee for leverage.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: This stretch may cause a few pops in your back, but that’s perfectly normal as long as there’s no pain.
7. Child’s Pose Stretch
The child’s pose is a classic yoga stretch that targets the entire back, especially the lats and spine.
How to Do It:
- Start on all fours (hands and knees).
- Sit your hips back toward your heels while reaching your arms forward.
- Tuck your chin into your chest and sink into the stretch, feeling the lengthening in your back.
- Hold for 30 seconds.
Tip: Breathe deeply and let your body relax into the stretch for maximum benefit.
8. Upper Back Extension
This movement opens up the chest and stretches the upper back, perfect for counteracting poor posture from sitting.
How to Do It:
- Sit or stand with your fingertips behind your head.
- Bring your elbows together and fold forward slightly.
- Then, lift your chest and elbows up, opening through your upper back and chest.
- Repeat this movement three times.
Tip: This dynamic stretch is excellent for improving posture and chest mobility.
9. Upper Traps Stretch
The trapezius muscles in the neck and upper back can get very tight, especially if you spend a lot of time hunched over a computer or phone.
How to Do It:
- Tilt your head to the left, bringing your left ear toward your left shoulder.
- Use your left hand to gently apply pressure to the right side of your head.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Tip: Keep the stretch gentle—this is a sensitive area, and too much pressure can cause discomfort.
Plyometric Exercises
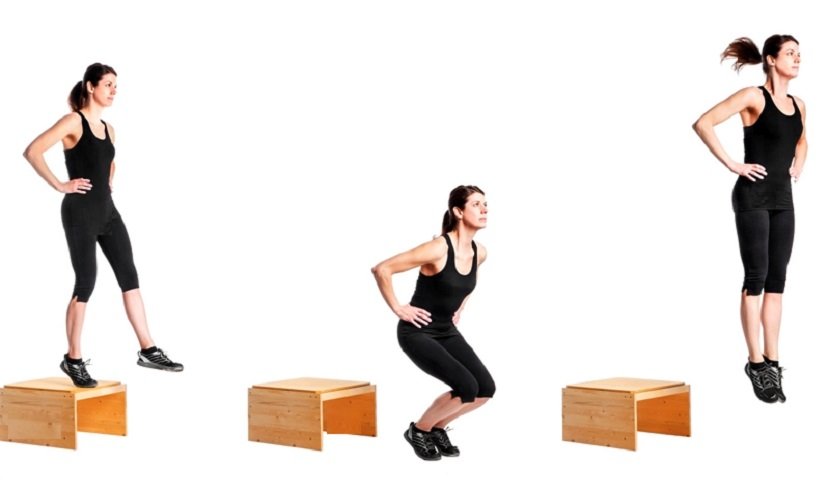

Box Jumps
Box jumps enhance explosive power. Athletes use box jumps to improve vertical leap and agility. The exercise involves jumping onto a raised platform. Box jumps require coordination and strength. Consistent practice increases muscle power and reduces injury risk.
Depth Jumps
Depth jumps focus on rapid force production. Athletes step off a box and immediately jump upon landing. This exercise trains muscles to react quickly. Depth jumps improve neuromuscular efficiency. Athletes gain better performance in sports requiring quick direction changes.
Olympic Weightlifting
Clean and Jerk
The clean and jerk builds total body power. Athletes lift a barbell from the ground to overhead. This movement combines strength and speed. The clean and jerk enhances muscle power and coordination. Regular training improves athletic performance in explosive sports.
Snatch
The snatch develops explosive strength. Athletes lift a barbell from the ground to overhead in one motion. This exercise requires precision and power. The snatch increases muscle power and flexibility. Athletes benefit from improved performance in dynamic sports activities.
Sprint Training
Short Distance Sprints
Short distance sprints boost speed and power. Athletes run at maximum effort for short distances. This training enhances fast-twitch muscle fibers. Short sprints improve acceleration and agility. Athletes gain an edge in sports demanding quick bursts of speed.
Hill Sprints
Hill sprints increase lower body strength. Athletes sprint uphill to build muscle power. This exercise challenges endurance and explosiveness. Hill sprints improve cardiovascular fitness and leg strength. Athletes experience enhanced performance in endurance-based sports.
Case Studies show that integrating these Muscle Power Workouts for Athletes leads to significant improvements. Research highlights the effectiveness of combining strength and ballistic-power training. Athletes achieve better results through targeted programs. These workouts reduce injuries and enhance overall performance.
Programming Ideas for Power Development
Periodization Techniques
Linear Periodization
Linear periodization involves a structured progression in training intensity. Athletes start with high-volume, low-intensity workouts. Over time, the focus shifts to low-volume, high-intensity sessions. This method enhances muscle power by gradually increasing the load on muscles. Research shows that linear periodization can lead to significant strength gains. Coaches often use this technique to prepare athletes for peak performance during competitions.
Undulating Periodization
Undulating periodization offers more variation in training. Athletes alternate between different intensities and volumes within a week. This approach prevents training plateaus and keeps workouts engaging. Studies indicate that undulating periodization can produce similar strength gains as linear models. Athletes benefit from the flexibility and adaptability of this method. Coaches can tailor programs to meet specific needs and goals.
Integrating Power Workouts into Training
Weekly Training Schedule
A well-structured weekly training schedule maximizes power development. Athletes should include a mix of strength, speed, and endurance sessions. Each week might feature two to three power-focused workouts. These sessions could involve plyometrics, Olympic lifts, or sprint drills. Rest days are crucial for recovery and muscle growth. Monitoring progress helps in adjusting the schedule for optimal results.
Balancing Power and Endurance
Balancing power and endurance is essential for comprehensive athletic performance. Athletes should incorporate both elements into their training regimen. Power workouts enhance explosive strength and speed. Endurance sessions build stamina and cardiovascular health. A balanced approach ensures athletes maintain peak performance across various sports demands. Coaches can design programs that integrate both aspects effectively.
-

 News2 years ago
News2 years agoKolkata Doctor Case: Tragic Story of Dr. Moumita Debnath
-

 Health And Fitness2 years ago
Health And Fitness2 years agoPepsi Zero Sugar vs Diet Pepsi: Which Is Healthier?
-

 Health And Fitness1 year ago
Health And Fitness1 year agoWhere to Find Oreo Flavored Coke Zero Near You
-

 Health And Fitness1 year ago
Health And Fitness1 year agoHow to Choose a Rehab for Lasting Recovery
-

 Tech Innovation2 years ago
Tech Innovation2 years agoTop Machine Learning and Deep Learning Trends for 2024
-

 News2 years ago
News2 years agoLondon King Opens Up About Her Relationship with Rob Schneider
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoTyra Banks Biography: Age, Husband, Net Worth
-

 Tech Innovation1 year ago
Tech Innovation1 year agoHuawei Mate XT: A Detailed Review of the World’s First Tri-Fold Smartphone